


Next: Multi-Time Step Nodal Subcycling
Up: 1-D ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
Previous: 1-D ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
Contents
Typical 1-D problems involve bars or beams under
axial loading. In order to test our various algorithms we define
a reference problem composed of a beam fixed at one end and free and the other
with an applied axial load at the free end, as seen in
Figure 3.1.
We use this general problem for all of our analyses in the
upcoming sections.
Figure 3.1:
Reference problem in 1-D.
|
|
This beam, of length 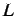 , is fixed at the right end
and has a compressive axial force applied on the left,
corresponding to an axial stress
, is fixed at the right end
and has a compressive axial force applied on the left,
corresponding to an axial stress
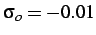
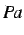 . The beam is homogeneous
and has a cross-sectional area
. The beam is homogeneous
and has a cross-sectional area 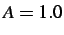
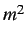 , density
, density
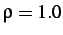
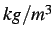 and Young's modulus
and Young's modulus 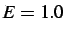
 .
The beam wave speed given by
.
The beam wave speed given by
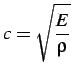 |
(3.1) |
is thus 
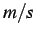 .
.
In 1-D the analytical solution to a beam problem can be
obtained by solving the wave equation
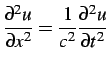 |
(3.2) |
with initial conditions
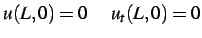 |
(3.3) |
and boundary conditions
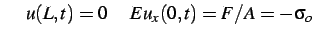 |
(3.4) |
where 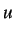 is the displacement and
is the displacement and 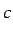 is the wave speed.
is the wave speed.
The solution to this problem is represented by the x-t (displacement-time) diagram
in Figure 3.2.
The displacement, velocity and stress profiles, for a sample point at 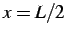 ,
are shown in Figure 3.3.
,
are shown in Figure 3.3.
Figure 3.2:
x-t diagram in 1-D.
Figure 3.3:
Analytical solution for displacement , velocity 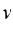 and stress
and stress
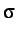 in the middle of the beam for the 1-D wave problem described in
Figure 3.1.
in the middle of the beam for the 1-D wave problem described in
Figure 3.1.
|



Next: Multi-Time Step Nodal Subcycling
Up: 1-D ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
Previous: 1-D ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
Contents
Mariusz Zaczek
2002-10-13
![\includegraphics[scale=0.6]{smol_bar_1.eps}](img265.png)
![]() , is fixed at the right end
and has a compressive axial force applied on the left,
corresponding to an axial stress
, is fixed at the right end
and has a compressive axial force applied on the left,
corresponding to an axial stress
![]()
![]() . The beam is homogeneous
and has a cross-sectional area
. The beam is homogeneous
and has a cross-sectional area ![]()
![]() , density
, density
![]()
![]() and Young's modulus
and Young's modulus ![]()
![]() .
The beam wave speed given by
.
The beam wave speed given by
![]() ,
are shown in Figure 3.3.
,
are shown in Figure 3.3.
![\includegraphics[scale=0.5]{xt_1d.eps}](img278.png)
![\includegraphics[scale=0.5]{analyticsol.eps}](img279.png)